In an era where visual data is exploding, organizations face a critical challenge: how to efficiently process and analyze massive amounts of video and image data without overwhelming their networks or breaking their budgets. Enter edge computing for computer vision – a game-changing approach that’s revolutionizing how we handle visual intelligence.
Understanding Edge Computing in Computer Vision
Edge computing brings data processing closer to where visual data is captured, rather than sending everything to distant cloud servers. Imagine a security camera that can analyze suspicious behavior right at the camera itself, or a manufacturing robot that can detect defects in real-time without consulting a central server.
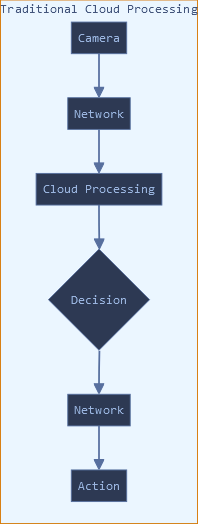
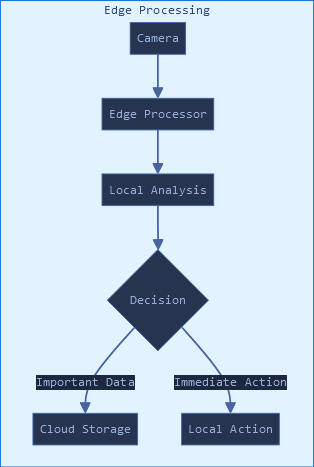
Figure 1: Edge vs. Cloud Processing Flow Comparison of traditional cloud-based processing versus edge computing architecture for computer vision applications.
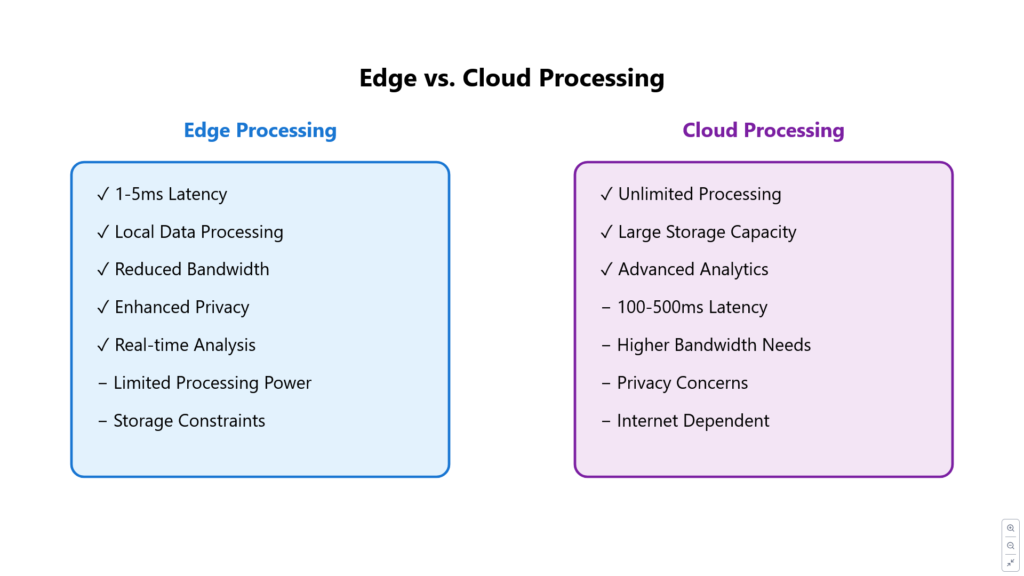


Figure 2: Edge vs. Cloud Processing Comparison A detailed comparison of edge and cloud processing approaches, highlighting the key differences in latency, processing capabilities, and data handling.
The Critical Advantages of Edge-Based Vision Systems
1. Real-Time Processing Speed
When milliseconds matter, edge processing delivers. By eliminating the round trip to cloud servers, edge-based vision systems can:
⦁ Provide instant analysis for time-critical applications
⦁ Enable real-time decision making
⦁ Reduce latency from seconds to milliseconds
2. Bandwidth Optimization
Edge processing significantly reduces network traffic by:
⦁ Processing raw visual data locally
⦁ Sending only relevant insights to the cloud
⦁ Minimizing unnecessary data transfer
3. Enhanced Privacy and Security
Processing visual data at the edge offers superior privacy protection:
⦁ Sensitive visual information stays local
⦁ Reduced risk of data interception during transfer
⦁ Compliance with data protection regulations becomes easier
4. Cost Efficiency
Edge computing can substantially reduce operational costs through:
⦁ Lower cloud computing expenses
⦁ Reduced bandwidth requirements
⦁ Decreased storage needs for raw data
Common Applications of Edge-Based Computer Vision
Manufacturing and Quality Control
⦁ Real-time defect detection on production lines
⦁ Immediate quality assurance checks
⦁ Automated process optimization
Smart Cities and Traffic Management
⦁ Intelligent traffic flow analysis
⦁ Real-time parking space monitoring
⦁ Emergency incident detection
Retail Analytics
⦁ In-store customer behavior analysis
⦁ Inventory management
⦁ Queue monitoring and management
Security and Surveillance
⦁ Immediate threat detection
⦁ Real-time perimeter monitoring
⦁ Automated access control

Figure 3: Processing Latency Comparison Side-by-side comparison of processing times for edge computing versus cloud-based solutions.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Hardware Considerations
To implement edge-based vision systems effectively:
⦁ Choose appropriate processing hardware for your needs
⦁ Consider power consumption requirements
⦁ Plan for environmental conditions
Software Optimization
Successful edge deployment requires:
⦁ Efficient model optimization for edge devices
⦁ Regular updates and maintenance procedures
⦁ Robust error handling mechanisms
Integration Strategies
⦁ Develop clear data flow architecture
⦁ Establish reliable connectivity fallbacks
⦁ Create robust data synchronization protocols
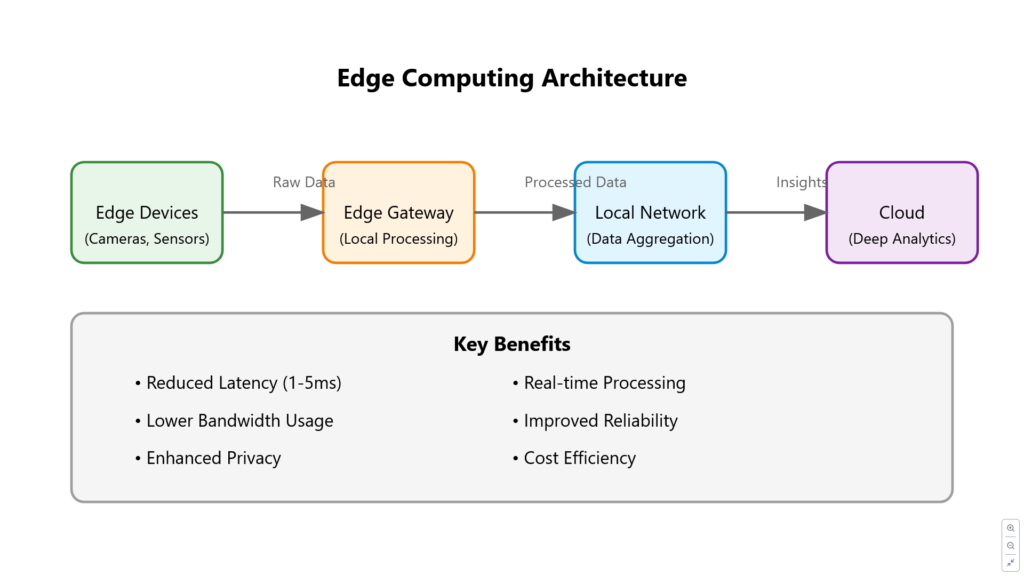
Figure 4: Edge Computing Architecture and Benefits Comprehensive overview of edge computing architecture showing data flow from edge devices to cloud, along with key benefits.
Best Practices for Edge Vision Implementation
1. Start Small and Scale
⦁ Begin with pilot projects
⦁ Validate performance metrics
⦁ Expand based on proven success
2. Balance Edge and Cloud
⦁ Determine optimal processing distribution
⦁ Maintain cloud connectivity for complex analysis
⦁ Implement hybrid solutions where appropriate
3. Future-Proof Your System
⦁ Choose scalable hardware platforms
⦁ Use updateable software architecture
⦁ Plan for increasing data volumes
The Future of Edge Vision Systems
The technology continues to evolve with:
⦁ More powerful edge processing units
⦁ Advanced AI capabilities at the edge
⦁ Improved energy efficiency
⦁ Greater integration with 5G networks
Making the Decision: Is Edge Vision Right for You?
Consider these factors:
⦁ Application latency requirements
⦁ Privacy and security needs
⦁ Available network infrastructure
⦁ Budget constraints
⦁ Scaling plans
Conclusions leo.
Edge computing in computer vision represents a fundamental shift in how we process and analyze visual data. As organizations strive for faster, more efficient, and more secure visual intelligence solutions, edge processing becomes not just an option, but a necessity for staying competitive in an increasingly visual world.

