The Evolution of IT Support: Why LLMs Matter
The enterprise IT support landscape has dramatically shifted with the advent of Large Language Models (LLMs). Traditional support methods often struggle with scalability and response times, while modern LLMs offer unprecedented capabilities in understanding and resolving technical issues.
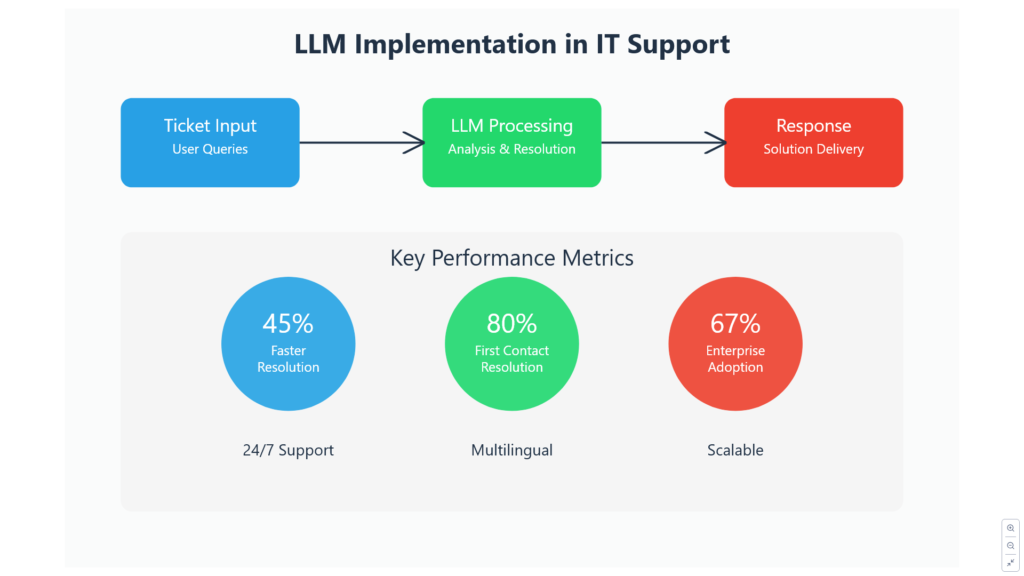
Key market statistics:
⦁ 67% of enterprises are exploring LLM implementation
⦁ 45% reduction in average ticket resolution time
⦁ 80% improvement in first-contact resolution rates
Understanding LLM Integration Points
Enterprise IT support systems can leverage Large Language Models (LLMs) at multiple touchpoints to enhance efficiency and user experience
1. First-Line Support
⦁ Automated ticket classification: Quickly categorizing incoming tickets to route them to the appropriate team.
⦁ Immediate response generation: Providing instant answers to common queries.
⦁ Knowledge base querying: Efficiently searching and retrieving information from the knowledge base.
⦁ Basic troubleshooting steps: Guiding users through simple problem-solving processes.
2. Complex Problem Resolution
⦁ Pattern recognition across historical tickets: Identifying recurring issues and patterns for quicker resolution.
⦁ Solution recommendation based on past resolutions: Suggesting fixes based on similar past issues.
⦁ Technical documentation synthesis: Compiling and summarizing technical documents.
⦁ Code snippet generation and debugging assistance: Assisting with coding tasks and debugging issues.
Implementation Strategy and Best Practices
A successful LLM implementation requires careful planning and execution. Consider these essential components:
Infrastructure Requirements
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.⦁ Secure API endpoints: Ensuring secure access to LLM services.
⦁ Data encryption protocols: Protecting data during transmission and storage.
⦁ Load balancing capabilities: Managing high volumes of requests efficiently.
⦁ Redundancy systems: Ensuring system reliability and uptime.
Data Security and Privacy Protecting sensitive information is crucial when implementing LLMs:
⦁ Implement proper data sanitization: Removing personally identifiable information and other sensitive data.
⦁ Establish clear data handling policies: Defining how data should be processed and stored.
⦁ Use encryption for data transmission: Securing data as it moves across networks.
⦁ Regular security audits: Continuously monitoring and improving security measures.
⦁ Compliance monitoring systems: Ensuring adherence to relevant regulations and standards.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit. Ut elit tellus, luctus nec ullamcorper mattis, pulvinar dapibus leo.
Integration Scenarios and Use Cases
1. Automated Ticket Resolution Modern LLMs can handle various support scenarios:
⦁ Password resets and account access issues: Automating routine password and account recovery tasks.
⦁ Software installation guidance: Providing step-by-step installation instructions.
⦁ Network connectivity troubleshooting: Offering solutions for common network issues.
⦁ System performance optimization: Suggesting ways to improve system performance.
⦁ Basic security incident response: Addressing minor security concerns promptly.
2. Knowledge Management LLMs excel at organizing and retrieving information:
⦁ Dynamic knowledge base updates: Keeping the knowledge base current with the latest information.
⦁ Real-time documentation generation: Creating and updating documents on the fly.
⦁ Technical document summarization: Condensing lengthy technical documents into concise summaries.
⦁ FAQ automation: Generating and updating frequently asked questions.
⦁ Process documentation: Documenting internal processes and procedures.
Measuring Success and ROI
Track these key performance indicators to measure success and return on investment:
1. Quantitative Metrics
⦁ Average resolution time: The time taken to resolve an issue.
⦁ First-contact resolution rate: The percentage of issues resolved during the first interaction.
⦁ Ticket volume reduction: The decrease in the number of tickets requiring human intervention.
⦁ Cost per ticket: The cost associated with resolving each ticket.
⦁ Customer satisfaction scores: Feedback from users on their support experience.
2. Qualitative Improvements
⦁ Support team satisfaction: The impact on support staff morale and job satisfaction.
⦁ Knowledge retention: The improvement in retaining and utilizing knowledge.
⦁ Process standardization: The consistency of processes and procedures.
⦁ Service quality consistency: The uniformity in the quality of support provided.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Implementation Challenges
1. Technical Integration
⦁ Solution: Use standardized APIs and middleware to facilitate integration.
⦁ Implement proper error handling: Ensuring systems can gracefully handle errors.
⦁ Establish robust monitoring systems: Continuously monitor system performance and issues.
2. Team Adoption
⦁ Provide comprehensive training: Equip staff with the knowledge and skills to use new tools effectively.
⦁ Create clear usage guidelines: Define how and when LLM tools should be used.
⦁ Establish feedback loops: Continuously gather and act on feedback from users.
⦁ Monitor usage patterns: Track how the tools are being used and identify areas for improvement.
Data Quality and Maintenance
Maintaining high-quality data is crucial:
⦁ Regular data cleaning and validation: Ensuring data accuracy and relevance.
⦁ Continuous model training and updates: Keeping the LLM up-to-date with the latest data and trends.
⦁ Performance monitoring: Tracking the performance of LLMs to ensure they are delivering value.
⦁ User feedback incorporation: Using feedback to refine and improve LLM capabilities.
Future Trends and Innovations
The future of LLMs in IT support looks promising:
1. Advanced Capabilities
⦁ Multimodal support (text, ⦁ image, ⦁ voice): Handling support requests in various formats.
Predictive issue resolution: Anticipating and resolving issues before they occur.
⦁ Automated code generation: Assisting with coding tasks and development.
Real-time language translation: Providing support in multiple languages instantly.
2. Integration Improvements
⦁ Better API management: Improving the efficiency and usability of APIs.
⦁ Enhanced security features: Strengthening security measures to protect data.
⦁ Improved customization options: Allowing for more tailored implementations.
⦁ Seamless scaling capabilities: Enabling the system to handle increasing loads effortlessly.
Best Practices for Enterprise Implementation
Planning Phase
⦁ Conduct thorough needs assessment: Understand the specific needs and goals of your organization.
⦁ Define clear success metrics: Establish how success will be measured.
⦁ Establish implementation timeline: Plan the phases of implementation with realistic timelines.
⦁ Identify key stakeholders: Ensure all relevant parties are involved and informed.
Execution Phase
⦁ Start with pilot programs: Test the implementation on a small scale before full deployment.
⦁ Gather continuous feedback: Regularly collect and act on feedback from users.
⦁ Monitor performance metrics: Track key metrics to ensure the implementation is meeting goals.
⦁ Adjust implementation strategy: Be prepared to make changes based on performance and feedback.
Conclusion
LLMs represent a transformative opportunity for enterprise IT support. Success requires careful planning, robust implementation, and continuous monitoring. Organizations that effectively deploy these tools can achieve significant improvements in support efficiency and user satisfaction.